Here is a brief history of the evolution of access control credentials
Magstripe cards
In the eighties, there was a swipe cards technology, also called a magstripe cards. This technology requires a manual swipe of the card through the reader in order to transfer its credentials to the access control systems
Magstripe cards are easy to activate and cost-effective, but they carry the great vulnerability, as they do not have any encryption. Moreover, they can demagnetize and cause complications for access control administration
Proximity cards
The invention of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) has been a game changer in the security system credentials. With the RFID technology, the contact between the reader and the card are no longer necessary. The data transmits through radio frequencies, 125 MHz (low frequency) or 13.56 MHz (high frequency).
- 125 MHz VS 13.56 kHz
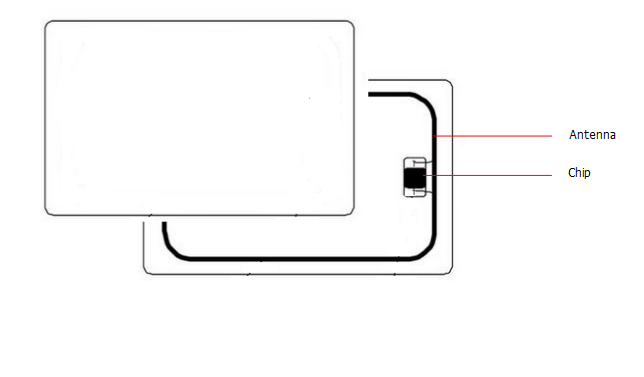
125 MHz (low frequency) is a first generation of proximity technology cards. In this case, a card has a physical chip. It receives power when approached to the reader by inducing electromagnetic waves to its antenna. As a result, the card responds by sending a signal, which is the card ID. It includes the facility code and the card number that is associated to the user.
| Card format | Facility code range | Card number range |
| 26 bits card | 0 to 255 | 0 to 65 535 |
| 34 bits card | 0 to 65 535 | 0 to 65 535 |
| 37 bits card | 0 to 65 535 | 0 to 524 287 |
Drawbacks Prox cards are read only cards. There is no encryption, very cost-effective cards but easy to hack or clone. These cards also do not have the ability to store additional information.
Smart cards
- 13.56 MHz (high frequency)
It is a second RFID generation of proximity cards technology. The cards using this technology are called smart cards. They can store up to 1Kb of additional information. They are also designed to keep the information safe by utilizing encryption keys. Moreover, Data is not emitted by the card until the card and the reader authenticate each other.
Examples of smart cards MIFARE cards, DESFire cards, IClass cards, Seos cards
Mobile access control credentials
It was seen as the next generation of credentials, but it is already here. Mobile devices are part of our everyday life. It is almost impossible to see someone who does not have a smartphone. As a result, smartphones, smartwatches are likely to replace cards.
Drawbacks Better to get your smartphone on charge all time
Read our posts