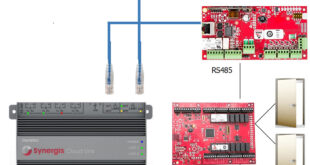
In many structured companies, physical access control is managed by the security department. So, security officers make the monitoring. Assign credentials to the employees, guests and visitors according to a security plan.
However, when it comes to small companies. The physical access control is often annexed to a department which is not busied by its normal operations. As a result, the physical access control is underused and reduced to its basic functions.
In this article, I am going to walk you through the main tasks of an access control manager. and the access control management.

Access control systems main functions
- The access control makes reports and tracks all users activities.
- Monitors on a real time door status and door alarms : forced doors, door open too long.
- Opens or closes doors remotely
- Implement schedules. It maintains doors open at certain times. Prevent from going in at other times. For example, no access after 6PM or on weekends.
- Eliminate traditional keys. No need to keep track of keys. No change of locks when someone loses a key. And when any employee quits, all you need to do is to delete him and cancel his card.
- Dynamic secure system.
- Simplified and flexible management. It is easy to edit access rights at any time. In other words, very easy to add or delete a user.
Each individual key can be deactivated if required and have access rights changed or removed. So there is no security risk If a key is lost or stolen
Access control management
The expectations of the system determine the functions to implement and the level of security to configure. Some institutions such as penitentiary institutions, government premises should require all the functions of a system. More than that, they could require to integrate the access control with the video surveillance system. Meanwhile, other customers would only expect the basic functions of the access control.
What an access control manager should know?
- Learn a system interface. Actually, the system communicates through the interface. All activities and events pop up on screen. The manager and the operator must observe all messages and acknowledge alarms and take the appropriate actions.
Trainings should help to optimize the use of a system, and better react to alarm, sabotage or trouble situations.
- Dispatch the appropriate actors. Authorities if it’s an emergency. A contractor if it’s trouble, or an operator or an officer to observe the incident.
- Be a member of an emergency plan and be aware of it.
What are the access manager main tasks ?
- Manage users and cardholders : Create, delete users and credentials.
- Manage partitions.
- Determine the access rules.
- Apply schedules on door and access points.
- Coordinate with installers and the security department.
- Make the access control system complies with the security plan of a company.
Read more about emergency plan
Users VS cardholders
Users
What is the difference between a user and a cardholder?
A user is an operator who uses the access control applications. A user can operate the system depending on the privileges he has.
User privileges
- application privileges: They determine the applications the user has access to. For instance, granting or denying access to the web application, to the configuration application.
- General privileges: This is about the generic features of the system. Like access to a printer to print reports. Access to read or modify a report…etc
- Administrative privileges : Grant access to the system configuration. We can name : access to entities or areas, schedule applications, and alarm management… etc
- Task and action privileges: They are privileges that control the tasks and the actions that a system could perform: investigation, arm or disarm zones …etc
Cardholders
A cardholder is any person who has a card and has access to some areas in the premises. He could be an employee, a visitor, a guest or deliverer or a contractor.
Access rights (Who, Where, When)
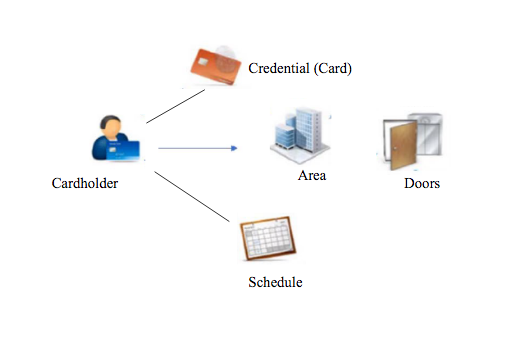
It is a combination of a valid card, representing a cardholder, an area where door are located. And schedules when a person has access. That implies Who, Where, When
A cardholder management requires every person to has a valid card. Represented in the system by its number.
You may also like our articles
Careers and position in security systems
The FICAM program is an access control manager for the US goverement.